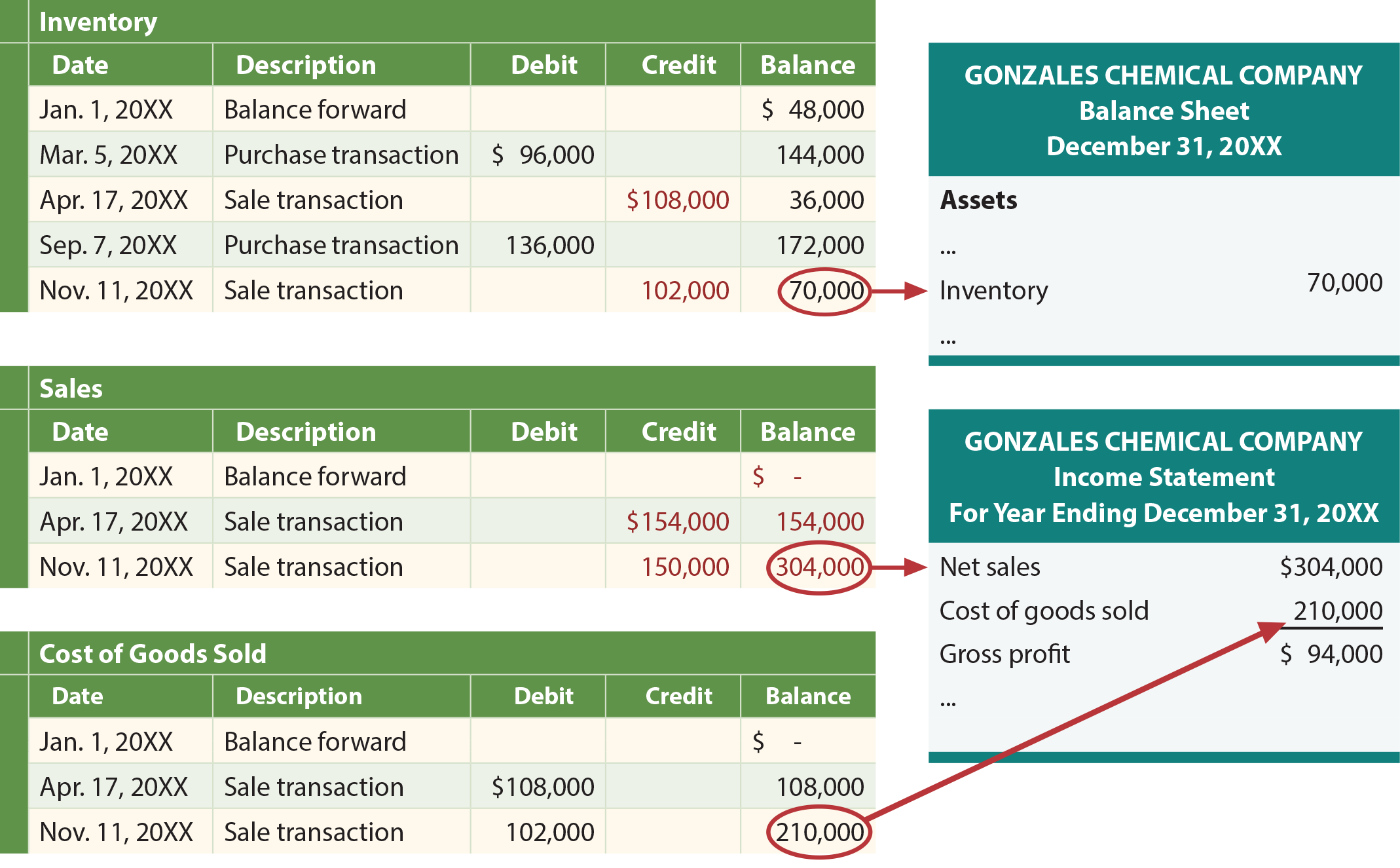
Companies debit their inventory account with the cost of the merchandise each time they purchase or produce inventory and when they sell inventory to customers. The perpetual inventory software updates the inventory account with each transaction. The three cost flow assumptions that businesses use for this are FIFO, LIFO, and the Weighted Average Cost (WAC).
Tech Advancements in Inventory Tracking
Inventory refers to any raw materials and finished goods that companies have on hand for production purposes or that are sold on the market to consumers. Both are accounting methods that businesses use to track the number of products they have available. The Weighted Average Cost (WAC) is the cost flow assumption businesses use to value their inventory. Also called the moving average cost method, accountants perform this differently in a perpetual system as compared to a periodic system. Most businesses would love to have updated inventory and COGS balances provided with a perpetual inventory system. However, constraints like difficulty in maintaining records and the need for powerful accounting software hinder some small businesses from using the perpetual inventory system.
- The cost of goods sold (COGS) account is also updated continuously as each sale is made.
- For example, Ava wants to figure out the average cost to assign for Acetone repackaged in her company’s warehouse.
- Both are accounting methods that businesses use to track the number of products they have available.
Calculations Using the Periodic Method
Perpetual inventory systems track sales constantly and immediately with computerized point-of-sale technology. Periodic inventory systems only track sales when a physical count is ordered and require a point-in-time count. The system allows for integration with other areas, including finance and accounting teams. Employees can use perpetual what can i deduct and what receipts should i keep for my taxes inventory data to provide more accurate customer service regarding the availability of products, replacement parts, and other physical components. System software provides real-time updates to inventory through the use of barcode scanners or other computerized records of product acquisition, sales, and returns as they occur.
Merchandising Transactions

As such, they use occasional physical counts to measure their inventory and the cost of goods sold (COGS). The perpetual inventory system keeps track of inventory balances continuously. This is done through computerized systems using point-of-sale (POS) and enterprise asset management technology that record inventory purchases and sales.
What Is LIFO Perpetual Inventory Method?
In contrast, a periodic LIFO system makes that same determination but not until December 31. Although these items were bought on September 22, which is after the last sale, they are included in the cost of goods sold for a periodic LIFO system. They offer scalability and accessibility, allowing businesses to manage inventory from anywhere, at any time.
Under either system, the allocation of goods available for sale to the cost of sales and ending inventory is the same if the inventory valuation method used is either specific identification or FIFO. Both systems will also result in different allocations to the cost of sales and ending inventory if the LIFO method is used in inventory valuation. Changes to inventory are usually recorded using either a periodic inventory system or a perpetual inventory system. In the perpetual inventory system, we record our purchases in the Inventory account rather than the Purchases account. In other words, we record inventory purchases as assets rather than expenses.
The scan triggers the inventory management system to automatically deduct the purchased units and update them as needed and will constantly track the stock level of each product. The perpetual inventory system is a method where inventory records are updated in real-time with each sale or purchase. This approach leverages barcode scanners and inventory management software, such as Oracle NetSuite or SAP ERP, to provide a continuously updated count of inventory. It allows for immediate insights into stock levels, which facilitates more responsive supply chain decisions and can enhance customer satisfaction through better stock availability. At the end of the period, a perpetual inventory system will havethe Merchandise Inventory account up-to-date; the only thing leftto do is to compare a physical count of inventory to what is on thebooks. A physical inventory count requirescompanies to do a manual “stock-check” of inventory to make surewhat they have recorded on the books matches what they physicallyhave in stock.
The Internal Revenue Service allows companies to use LIFO in their tax accounting, even when they use FIFO in their financial statements. Calculate the beginning inventory as whatever stock remains from the previous period if you do not have a true beginning inventory. The COGS in a perpetual system is rolling and recalculated after each transaction, but you can use the COGS formula to calculate it for a period. Perpetual and periodic systems require different tools and procedures around how employees document inventory, although they can be complementary. In a periodic system, employees record products only at specified intervals. The following example can help illustrate how the calculation of the cost of sales, gross profit, and ending inventory will differ under the four inventory valuation methods.
The cost of goods sold (COGS) account is also updated continuously as each sale is made. The information collected digitally is sent to central databases in real time. Perpetual inventory is computerized, using point-of-sale and enterprise asset management systems, while periodic inventory involves a physical count at various periods of time. The latter is more cost-efficient, while the former takes more time and money to execute. There were 5 books available for sale for the year 2023 and the cost of the goods available was $440.